随着“双碳”政策在各行各业的推行,水处理行业面临巨大的挑战,如何降低处理过程中的能耗、实现废物资源化回收,同时减少过程中的碳排放已成为整个行业面临的关键问题。”菌藻共生”水处理技术的提出,将藻类特有的利用光合作用进行的固碳功能以及对于氮、磷自身代谢吸收同功能菌群降解有机污染物的功能相结合,同时藻类过程中产生的氧气又能被菌类利用,实现了无机固碳、营养盐回收、降污建排三重目标。
烟台大学土木工程学院安众一、张慧超副教授、李丹博士课题组围绕“菌藻共生生物群落稳定构建”这一核心问题,针对不同的水质,设计反应器、筛选构建功能菌群、优化反应参数、扩大应用范围,以旋转式固定生物膜反应器和好氧菌藻颗粒污泥作为反应载体,成功应用于油田含聚废水、垃圾渗滤液、纺织行业染料废水、海水养殖废水等生物处理。相关研究成果已发表在环境领域国际知名期刊《Bioresource Technology》(中科院I区top,IF 11.4)、《Journal of Water Process Engineering》(中科院II区,IF 7.0)、《Frontiers in Microbiology》(中科院II区Top,IF 5.2)等期刊上,为实现高效的生物脱氮固碳模式提供了借鉴和思路。烟台大学为发表系列论文的第一作者单位和通讯作者单位,本课题得到了国家自然科学基金和山东省自然科学基金的资助。
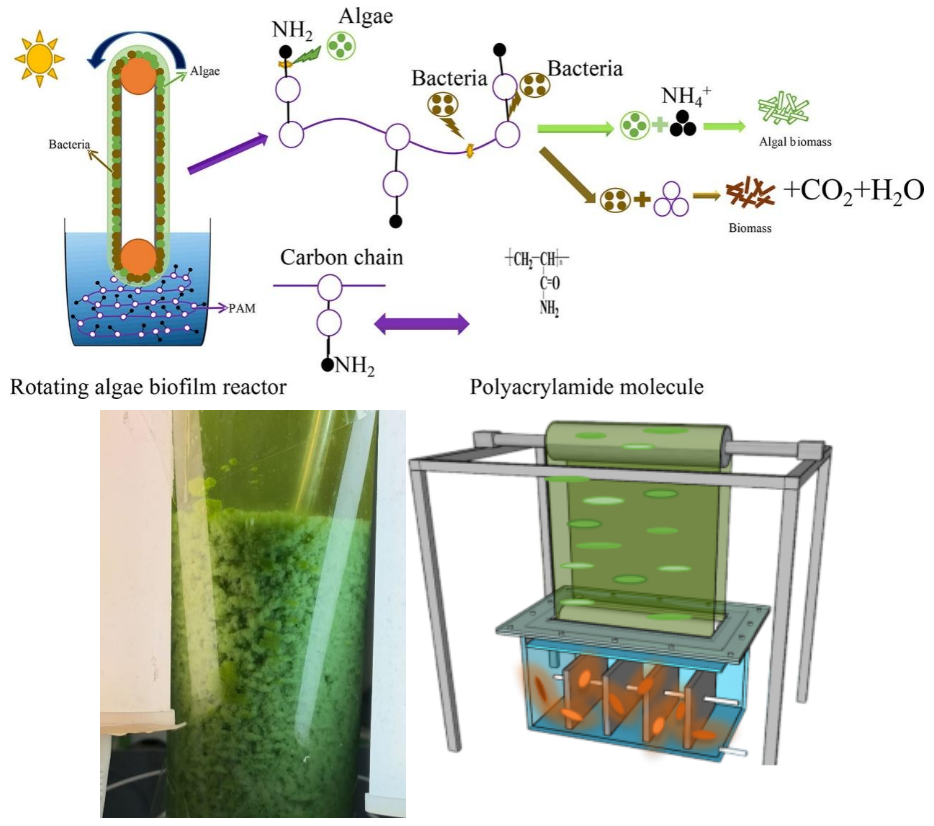
相应论文如下:
1.Treatment of polyacrylamide-polluted wastewater using a revolving algae biofilm reactor: Pollutant removal performance and microbial community characterization
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125132
2.A revolving algae biofilm based photosynthetic microbial fuel cell for simultaneous energy recovery, pollutants removal, and algae production
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.990807
3.Degradation efficiency of the azo dye acid orange 2 and microbial community characteristics in a rotating algal biofilm reactor
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103233
4.Construction of a mycelium sphere using a Fusarium strain isolate and Chlorella sp. for polyacrylamide biodegradation and inorganic carbon fixation
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1270658
5.The Characteristic Evolution of Simultaneous Removal of Organic Pollutants and Nutrients from Mariculture Wastewater Using a Rotating Algal Biofilm (Rab) System
http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4434905